Considered from a larger perspective, the operating cycle affects the financial health of a company by giving them an idea of how much its operations will cost, as well as how quickly it can pay its debts. Every industry works differently, which means that the length of this operating cycle can vary from one niche to another. Understanding your operating cycle can help you determine your financial health as it can give you a great indication of the company’s ability to pay off its liabilities in due course. The balance in the Income Summary account is transferred to retained earnings because the net income (or net loss) belongs to the shareholders.
Financial Modeling Solutions
- The business, through this calculation, can check the total time taken from receiving the inventory to storing them, selling them, and customers paying for them.
- It combines the time for inventory turnover and receivables collection minus the payables period.
- This procedure transfers the balance in the income summary to retained earnings.
- This cycle is a crucial measure of a company’s financial efficiency and liquidity.
- We’ll explore the formula and its basic concepts, as well as provide practical examples to help you grasp this critical aspect of your business.
This is computed by dividing 365 with the quotient of credit sales and average accounts receivable or receivable return. Although you must understand how to calculate the operating cycle if you want to compare yourself to your competitors, it is also important to understand what it really means for your business. LO6 – Explain the use of and prepare closing entries and a post-closing trial balance. The above adjusting entry enables the company to match the income tax expense accrued in January to the income earned during the same month. It indicates that a business converts inventory and receivables into cash more quickly, improving liquidity and reducing the need for external financing. This means it takes the company about 102.2 days to convert its inventory into cash through sales and collections.

Receivables collections
LO2 – Explain the use of and prepare the adjusting entries required for prepaid expenses, depreciation, unearned revenues, accrued revenues, and accrued expenses. As a result of this entry, salaries expense is reported on the January income statement when cash is paid. The matching of revenue to a particular time period, regardless of when cash is received, is an example of accrual accounting. Accrual accounting is the process of recognizing revenues when earned and expenses when incurred regardless of when cash is exchanged; it forms the basis of GAAP. Typically, a shorter operating cycle means a company converts inventory and receivables into cash more quickly.
LO1 – Explain how the timeliness, matching, and recognition GAAP require the recording of adjusting entries.

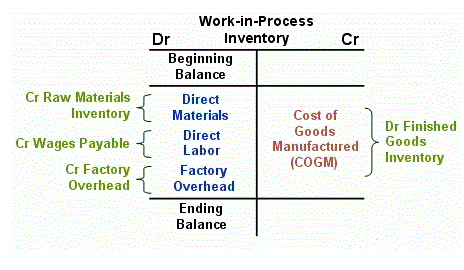
At the end of a fiscal year, after financial statements have been prepared, the revenue, expense, and dividend account balances must be zeroed so that they can begin to accumulate amounts belonging to the new fiscal year. Closing entries transfer each revenue and expense account balance, as well as any balance in the Dividend account, into retained earnings. Revenues, expenses, and dividends are therefore referred to as temporary accounts because their balances are zeroed at the end of each accounting period.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Explore our marketplace and find the perfect tool to streamline your processes today. To assist you in computing and understanding accounting ratios, we developed 24 forms that are available as part of AccountingCoach PRO. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. So, from the above-given data, we will first calculate the Inventory Period (days) of Apple Inc.
Notice that the $1,857 must agree to the retained earnings balance calculated on the statement of changes in equity. To review, a cost is recorded as an asset if it will be incurred in producing revenue in future accounting periods. A cost is recorded as an expense if it will be used or consumed during the current period to earn revenue. On the other hand, operating cycle formula a longer business operating cycle can strain cash flow, as money is tied up in inventory and receivables for an extended period. This can lead to cash shortages, making it challenging to pay bills, cover operating expenses, or seize new opportunities. A low DSI suggests that your company is efficiently managing inventory and selling products quickly.
Companies may decide its own accounting cycle based on the time schedules for financial reporting, whereas they must follow the actual business transaction process to determine what a particular operating cycle may be. The accounting cycle is the accounting process used to record business transactions in accounting books and supply the end-of-accounting-period financial statements. The operating cycle is the business transaction process in which business inventories are purchased, processed and eventually sold to customers. A company’s accounting cycle and operating cycle are independent of each other with respect to the length of the cycles, but they are also closely related in terms of information flow between the two areas. The adjusted trial balance is prepared using the account balances in the general ledger after adjusting entries have been posted. A negative operating cycle occurs when a company’s accounts payable (DPO) period is longer than the combined inventory days and days sales outstanding (DSO) periods.
An adjusted trial balance reports account balances after adjusting entries have been recorded and posted. An asset or liability account requiring adjustment at the end of an accounting period is referred to as a mixed account because it includes both a balance sheet portion and an income statement portion. The income statement portion must be removed from the account by an adjusting entry. Therefore, while the operating cycle focuses solely on the time to turn inventory into cash, the cash cycle provides a fuller picture by factoring in how long the company can delay payments to suppliers.

- Normal operating cycles are the usual time it takes for a business to turn inventory into cash.
- Monitoring these KPIs regularly and taking action to improve them can lead to a more efficient operating cycle, improved cash flow, and enhanced financial performance for your business.
- The truck and equipment purchased by Big Dog Carworks Corp. in January are examples of plant and equipment assets that provide economic benefits for more than one accounting period.
- Understanding and monitoring your operating cycle can help you identify areas for improvement, optimize cash flow, and make informed financial decisions.
- You’ll explore the components, calculation methods, practical strategies, key performance indicators, and the tools needed to master the art of optimizing your operating cycle for enhanced efficiency and profitability.
- The length of a company’s operating cycle can impact everything from their ability to finance new growth initiatives to the interest rates they’re offered on loans.
- The accounting cycle and operating cycle most likely do not coincide with each other.
It combines the time for inventory turnover and receivables collection minus the payables period. The operating cycle is a financial metric that measures the time it takes for a company to convert its investments in inventory and accounts receivable into cash. Essentially, it is the duration between the acquisition of inventory and the collection of cash from customers after selling the inventory. However, the length of an accounting cycle is not dependent on how and when business transactions take place, because a company can select the start and finish of its accounting cycle to carry out the required accounting tasks. An accounting cycle can be a calendar year or a fiscal year, and it can be also on a quarterly or monthly basis. Financial statements must be prepared in a timely manner, at minimum, once per fiscal year.

